Do you have a WordPress site that you want to grow?
You need to know about WordPress security and how to implement it on your site.
Without the right steps, your site could be unnecessarily vulnerable to cyberattacks.
If a hacker gets in, you could lose everything.
Fortunately, you can protect yourself by learning the basics.
Then, you can follow a few security tips to protect your site.
- Is WordPress Secure?
- Types of WordPress Vulnerabilities
- What Is WordPress Security?
- How to Secure a WordPress Site
- 1. Update Regularly
- 2. Remove Unused Themes and Plugins
- 3. Host Your Website on a Secure Host
- 4. Only Install Things From Trusted Developers
- 5. Use Secure Login Details
- 6. Change the WP-Admin URL
- 7. Install an SSL Certificate and Force SSL
- 8. Enable 2FA
- 9. Limit Login Attempts
- 10. Set Up Automatic Backups
- 11. Monitor User Activity
- 12. Scan for Malware
- 13. Disable PHP Error Reporting
- 14. Disable File Editing
- 15. Disable XML-RPC
- 16. Hide the WordPress Version
- 17. Block Hotlinking
- 18. Secure wp-config.php file
- 19. Use Captcha Verifications Where Possible
- 20. Add Security Headers
- 21. Implement WordPress Security Plugins
- 22. Use a VPN and Other Secure Connections
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Wrapping Up
Is WordPress Secure?
WordPress is secure to use provided that you follow a few best practices.
The team of developers works hard to fix WordPress security issues quickly.
However, you have to keep your site up to date as well.
Consider some vulnerabilities and how they can affect you.
Types of WordPress Vulnerabilities
WordPress vulnerabilities can vary from attacks to redirects.
The different vulnerabilities can go away with an update to the software.
Here’s what you should know about the vulnerabilities of WordPress.

1. Brute-Force Attacks
Brute-force attacks occur when a hacker uses trial and error to guess your login details.
An attacker can start by trying common usernames and passwords to access your site.
People and computers can try thousands of passwords per minute.
If a hacker WordPress won’t automatically block users for using wrong passwords.
2. Malicious Redirects
Another vulnerability is that hackers can insert code into your site.
They could apply code that would redirect visitors from your site to another, usually to get more impressions on ads.
In some cases, the redirects could cause more problems for you and your website visitors.
Plus, after you get your site back, you could have trouble rebuilding trust with your audience.
3. XSS (Cross-Site Scripting)
Cross-site scripting is similar in that it tries to redirect visitors to another site.
However, it uses JavaScript to collect data or redirect users to a scammy website.
4. DDoS Attacks
A DDoS (distributed denial of service) attack happens when a hacker sends a lot of traffic to a website.
The goal is to overload the server and cause it to crash.
What Is WordPress Security?
WordPress security refers to what developers and website owners can do to protect the websites that use the software.
You can do a lot more than you might expect to help keep your website safe.
Why Is WordPress Security Important?
WordPress security helps keep your site up and running.
You can also use it to reduce the risk of being a victim of brute-force attacks, DDoS attacks, and other issues.
How to Secure a WordPress Site
Despite the various vulnerabilities, you can protect your website.
The sooner you add security measures, the harder it will be for hackers to attack you.
Consider the following options to secure your WordPress site.
Then, you can start with one security option and go through the list.
Some of the following options are easy and only require a step or two.
However, others require a bit of coding, so you might want to hire a developer.
If you can’t do that, you can ask for help from your website host, or you can rely on other methods that you can implement without help.
Either way, here are some WordPress security tips you can try.

1. Update Regularly
One of the best things you can do is to update your website as soon as an update is ready.
At WordPress, the development team monitors security issues and attempts to fix them.
When they have a fix, they usually release it in the form of a new update.
The same is true of smaller elements of your website, such as your theme and plugins.
If you use an outdated version of any of those things, you can put your site at risk.
Hackers may have found vulnerabilities of older updates.
Be sure to check your website for updates at least once a week.
If you work on your site more often, check whenever you log into your admin dashboard.
That way, you’ll know if you need to perform any updates to secure your site.
As you check for updates, you should consider a few different types.
Here are a few things you need to update and how you can do so.
Update WordPress Itself
Of course, you need to update the WordPress core whenever there’s a new version.
You can usually do this through your updates page.
Look for an update to WordPress and start the process.
Another option is to follow the WordPress website or Twitter account to learn when there’s a new update.
However, it helps to backup your site and export a copy of it.
That way, you’ll be able to revert your site to the prior version if something goes wrong.
You can use a free backup plugin and store your backups on your computer or in the cloud.
Some website hosts might also offer to backup your site for you.
They could also help manage larger WordPress updates.
Consider if your host provides those services and how you can get the assistance you need.
Even if your host won’t automatically update your site, they could still help.
Contact your host’s customer service team, and someone might be able to walk you through the update process.
Don’t do anything with your site while it’s updating so that you don’t break it.
Update Version of PHP
PHP is the programming language that serves as the basis of WordPress.
Regularly updating your version of PHP can help keep your site secure, and it can help your site work better.
You can use a few different PHP versions, including a few older versions.
According to WordPress.org, you should use the newest version available.
They recommend at least PHP 7.4.
The newest version of WordPress also supports PHP 8.0 and PHP 8.1, but it’s still in beta, so it might not work well on every site.
While you can use older versions, you should at least update to 7.4.
The PHP community stopped supporting 7.3 near the end of 2021.
If security issues develop, the community won’t offer official solutions.
So even if you have the latest version of WordPress, your PHP version could keep your site from being as secure as possible.
Luckily, you can check your PHP version in the Site Health section of your dashboard.
You’ll need to go to your hosting account and follow their steps for updating PHP.
The exact steps can vary between hosting companies.
Update Themes and Plugins
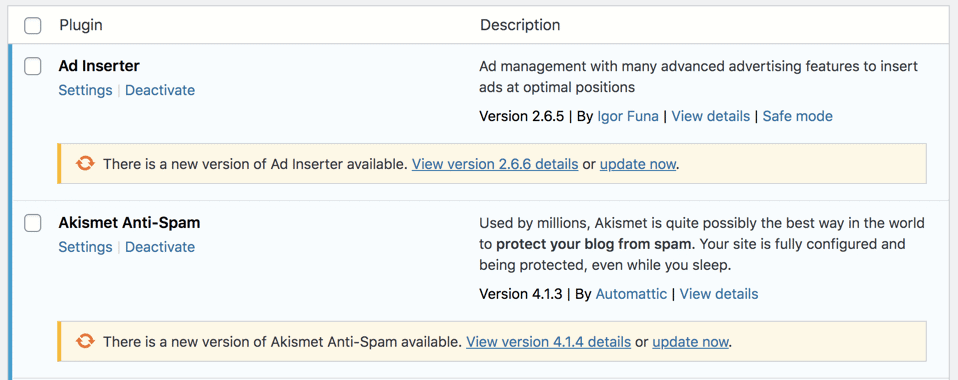
As you update WordPress and PHP, consider smaller parts of your site.
You’ll also occasionally need to update your website theme and plugins.
The developers might update their work to fix security problems or to add new features.
Even if the update just adds features, you should still update it.
Then, you can make sure you’re using a version that the developers will support.
If you use an older version, as with WordPress core, you could leave your site unnecessarily vulnerable.
To check for theme and plugin updates, go to your updates page in your dashboard.
You can see which themes and plugins have new versions.
Select all of the themes or all of the plugins to update them, but you can’t update both groups together.
Before you update a theme, consider any changes you’ve made.
If you’re making changes but not using a child theme, you’ll lose your edits with the next update.
You should also consider a backup before updating a theme or a lot of plugins.
Another thing to consider is enabling automatic plugin updates.
That can save you a lot of time, especially if you use many plugins on your site.
2. Remove Unused Themes and Plugins
When you go to update your plugins and themes, you may notice there are some you don’t use.
Instead of updating them, go to your Plugins page.
Click “Deactivate” under each plugin you never use.
Then, you can delete the plugins so that they aren’t taking up space on your site.
You can do the same thing for your themes by going to Appearance > Themes.
For any themes that you aren’t using, hover your mouse over the theme and click “Theme Details.”
Click on “Delete” to remove the theme from your site.
If you decide to switch back to a theme later, you can always reinstall it and activate it.
The same is true if you decide you want to use an old plugin in the future.
But if you don’t want to fully delete a plugin, you should at least deactivate it.
In addition to removing plugins and themes, only add the ones that you’ll use.
You might want to test out a plugin or theme, and you can do that.
However, don’t forget to delete it if you decide not to use it.
If you switch themes, delete the old theme once you activate the new one.
3. Host Your Website on a Secure Host
Your website host can have a bigger effect on WordPress security than you might expect.
As you choose a host, consider what security features they offer.
Look at what you’ll get with a hosting plan, such as automatic backups and updates.
You can also consider if a host will offer a security certificate.
Be sure to compare a few WordPress hosts to see what they offer and for what price.
That way, you’ll be able to get the best deal that meets your needs.
Also, you should research the company’s average uptime percentage.
If a host goes down a lot, it could be that the host isn’t the most secure.
Some attacks can keep your site from running properly.
Another essential factor to consider is the host’s customer service.
If your site does experience an attack, you’ll want the host’s help to get the site back as soon as possible.
A host with good customer service can be well worth it for the peace of mind in case an attack occurs.
4. Only Install Things From Trusted Developers
When choosing WordPress themes and plugins, do your research.
As you look at your options within WordPress, you’ll be able to see a few things.
You can see things like the name of the plugin and the name of the developer.
The plugin page also shows you the average star rating from reviews and the number of active installations.
You can see if the plugin is compatible with your WordPress version and when the developers last updated the software.
Look at the name of the developer and search for them on Google.
Then, you can figure out if they’re trustworthy and if they make other useful plugins.
It also helps to install plugins that have a lot of active users as well as those with good reviews.
If you find a plugin’s last update isn’t compatible with WordPress, that’s a bad sign.
Some plugins may say they’re untested, so you could use them, but it will be a risk.
You should also learn more about themes before installing them.
5. Use Secure Login Details
Another vital aspect of WordPress security is your login credentials.
You need to choose a good username as well as a nice password.
Sadly, you can’t change your username after you create your profile, so try to create a username other than “admin” since it’s easy to guess.
If you already have that as your user, create a new user account with a more secure username.
Give the new account full administrative positions, and delete the original account.
That way, you can keep hackers from guessing the password.
If you must keep the account, use a password that would be almost impossible to guess.
Of course, you’ll also want to choose a secure password for other accounts, and you can change your password.
Be sure your password uses a mix of capital and lowercase letters.
Include a few numbers and even a special character or two (such as ! or @).
A good password should include at least eight characters, and longer passwords are even better.
You can even swap out characters for similar characters.
For example, use the number 0 instead of the letter O, or use an @ instead of the letter A.
Another option is to base your password on a phrase.
Use the first letter of each word in the phrase, and add those character swaps to make it even more secure.
To make it unique to your website, add the first letter of your website to the beginning of the password.
6. Change the WP-Admin URL
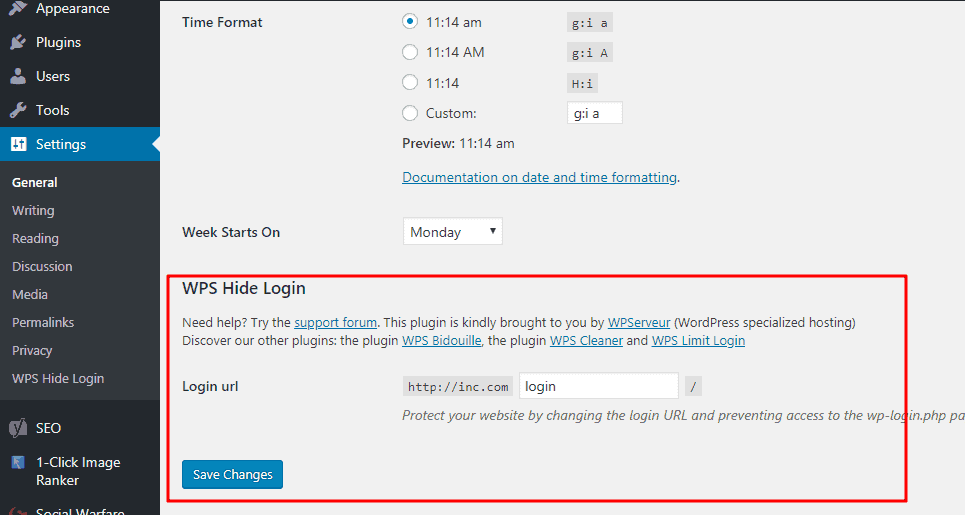
The default webpage for logging into your dashboard is www.yoursite.com/wp-admin.
However, you can use a plugin such as Change wp-admin login to change the URL.
The plugin won’t mess with the files in WordPress core.
However, changing the URL can make it harder for hackers to find the login page.
Since the default /wp-admin applies to all WordPress sites, all a hacker needs to do is add that to the end of your site.
Then, they can start guessing your login details.
You can change the URL to something much more difficult to guess.
Then, you’ll still know where to go to get into your site.
If you have others who write for your site or edit, you can give them the correct address.
However, it won’t be easy for a random attacker to get to.
You can also set up a redirect from the wp-admin page to your homepage or another page on your site.
Of course, you’ll want to keep a record of the new login page so that you can get in.
7. Install an SSL Certificate and Force SSL
A secure sockets layer (SSL) certificate is what turns the HTTP before your domain into HTTPS, and it makes your website more secure. It encrypts your website to protect your data and that of your website visitors.
Some website hosts offer an SSL certificate for free with your hosting package.
Other companies charge extra, but that can be well worth the cost.
Another option is to install an SSL plugin to secure your site.
Be sure you keep your SSL certificate active to maintain the security.
You’ll also want to force SSL by redirecting traffic from HTTP to HTTPS.
You can use a plugin to help set up redirects or to force SSL specifically.
If you want to check if your site has an SSL, look at the full IRL.
The page should start with HTTPS, and you should see a padlock next to it in your browser bar.
Aside from security, using an SSL can help with SEO so that you rank higher on Google.
8. Enable 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is another fantastic option for WordPress security.
It requires you and other users to use two devices to log into your site.
That helps your website verify that you should have access.
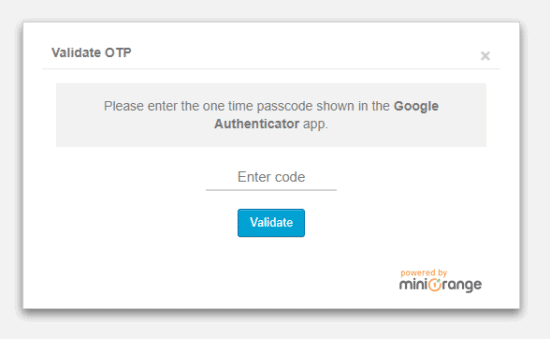
The easiest way to implement 2FA is to go to your dashboard and click Users > Profile.
Scroll down until you see the setting for 2FA Status.
Click on a button that says “Activate 2FA” or something similar since the specifics can depend on what plugins you use.
You might need to install a security plugin first.
Some general security plugins, such as Wordfence, include the feature.
If you don’t see the option to set up two-factor authentication, you can install a new plugin for it.
However, to help reduce the number of plugins, look for a more general security plugin.
If it has 2FA as a feature, you can set that up without taking up extra space on your site.
9. Limit Login Attempts
A fantastic way to protect your site from brute-force attacks is to limit the number of times you can enter incorrect credentials back to back.
You can use the Limit Login Attempts Reloaded plugin.
The plugin lets you control how many times you can enter a password before getting locked out.
You’ll also be able to set the timing for lockouts.
It will email you whenever someone tries to log into your site and doesn’t use the correct credentials.
You can even safelist and blacklist IP addresses.
Plus, you’ll see how many attempts you have remaining in case you or another person forgets their password.
That way, you can keep from locking yourself out of your WordPress site.
As you configure the settings, give yourself a few attempts to get your password correct.
It can be easy to forget your login, so you don’t want to block yourself after one try.
Three attempts is usually a good number.
10. Set Up Automatic Backups
You can do a lot of things to protect your website, but you could still experience an attack.
In case that happens, you’ll want to have a recent backup of your website.
While you can manually backup your site, consider setting up something automatic.
A few website hosts will backup your site for you, so you might not need to do anything.
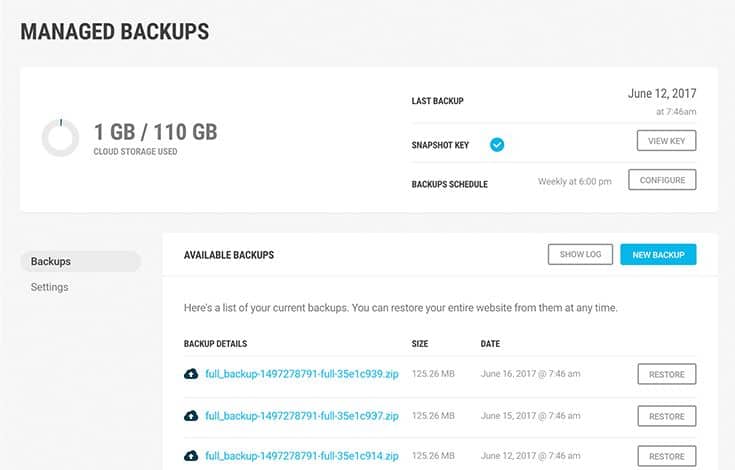
If your host or plan doesn’t include backups, you can install a backup plugin.
Even when your host backs up your site, it helps to do so yourself as well for extra security.
Look for a plugin that lets you schedule backups regularly.
Consider if you can download the backups to your computer or if you can store them in the cloud.
Having a backup will be critical if a hacker takes over your site.
The attack could affect your data, so you’ll want a copy of your site to get it back to normal.
Otherwise, you could lose media, blog posts, and pages.
11. Monitor User Activity
You can also start monitoring the activity on your website.
That way, you can catch suspicious activity when it occurs, and you can stop it.
WordPress has tons of plugins to choose from that monitor your website.
Wordfence is a more general plugin that emails you whenever someone logs into your site.
It will tell you the username, IP address, hostname, and location.
That way, you can learn when someone accesses your site when they aren’t supposed to.
So you might learn someone tries to access your site from a strange location.
If you know that wasn’t an authorized user, you can take steps to recover your site.
Then, you can implement more WordPress security measures to prevent the issue in the future.
You might be able to monitor activity manually, but technology is much more helpful.
It could catch activity that you miss.
Then, you can figure out if the activity is good or if you need to do something to stop an attack.
12. Scan for Malware
Another thing to do is to scan your website for malware, and Wordfence works great.
You should scan your site at least once per month.
Scan your site even if you don’t notice any signs of malware, because malware can stay on your site for a while before it causes problems
Before you conduct a scan, backup your site and download a copy.
Then, head to Wordfence > Scan, and click on “Start New Scan.”
If Wordfence detects any issues, you can then click “Delete All Detectable Files.”
Alternatively, you can review the details of each issue and delete files accordingly.
You don’t want to just delete anything the scan detected.
While it can work well, it might also have a false positive, so you could delete something you need.
If you find any malicious files, delete them right away.
You might also want to watch your site more to make sure new files don’t appear.
Then, take other steps to secure your site so that other hackers don’t attack you.
13. Disable PHP Error Reporting
You might also want to disable PHP error reporting, especially if you’re not a developer.
If you don’t get rid of the errors, it won’t get your site from running.
However, the errors could appear publicly to visitors, including potential hackers.
To get rid of the reporting, you need to change your wp-config.php file.
Look for something that says define(‘WP_DEBUG’, true;).
The code might have “false” in place of “true” so look for that as well.
Then, you can insert the following code to fix the problem:
ini_set('display_errors','Off');
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL );
define('WP_DEBUG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);If you’re not a developer, you may want to hire one to do this for you so that you don’t mess anything up.
14. Disable File Editing
For developers using WordPress, it’s easy to edit the code of website files.
WordPress offers this setting to all websites, but it’s unnecessary for most people.
What’s more, not disabling file editing can allow hackers to input code on your site.
Look for a security plugin that will take away the option to edit files on your site.
Then, you can protect yourself from XSS and similar attacks.
If you or a developer needs to edit files, you can temporarily turn the plugin off.
Go in and add your changes, then turn the plugin back on.
You’ll be able to keep hackers from adding malicious code that could redirect visitors to a bad website.
15. Disable XML-RPC
WordPress uses XML-RPC to communicate with mobile and web apps.
The newer REST API is more secure, but XML-RPC still exists.
Sadly, it can make your website more vulnerable to attacks.
It’s a common choice for brute-force attacks, since the protocol can handle requests with many commands at once.
As long as you aren’t using it, you can disable XML-RPC to further protect your site.
Some general WordPress security plugins will disable the technology for you.
If yours won’t, you can install the Disable XML-RPC-API plugin.
16. Hide the WordPress Version
If you have yet to update to the newest WordPress version, you should hide your version.
A hacker could figure out the version of your site.
They might learn you’re using an older update, and they could make you an easy target for their next attack.
Hackers can discover your WordPress version through the WordPress readme file, RSS feed, or the page source.
To stop this, install and activate a plugin, like WP-Hardening.
Head to Security Fixers, and toggle on the setting that hides your WordPress version number.
You can also remove the number using code, but that’s risky for non-developers.
A plugin is the best option.
Of course, you should also update WordPress as soon as possible for more protection.
Some hackers might try any site, even if they can’t find the WordPress version.
Also, hackers might be smart and figure out why you’re hiding your version number.
So they might decide to attack your site, even if you have the most recent WordPress update.
17. Block Hotlinking

Hotlinking is when another site embeds your content to make it look like theirs.
However, unlike copying and pasting, your server responds when someone accesses the content.
You have to pay for that.
To stop this, you can block hotlinking in a few ways.
The easiest option is to install a plugin either for hotlinking or general security.
General plugins tend to work better since the specific plugins don’t have good maintenance.
You can use a plugin called Prevent Content Theft.
That can help protect against right clicks, which can be responsible for a lot of hotlinking.
Sadly, hotlinking isn’t illegal, but it can be costly to you as the site owner.
Of course, you can ask people who do it to stop.
If they don’t respond, though, you may need to block it to stop them and prevent future attacks.
18. Secure wp-config.php file
When you set up your WordPress website, it automatically created a wp-config.php file.
The file holds a lot of security information about your site.
If a hacker gets their hands on the file, they could damage your site significantly.
You can do a lot to help secure the file, so consider your options.
Some choices are better for your site than others.
Think about what you want to do and if someone has attempted to hack your site or not.
One option is to set file permissions so that only certain users can get to it.
Finally, you can secure the file using the .htaccess file.
This and most other options require a bit of coding, so consider hiring a developer to protect your site as you make changes.
Move the File
You can secure the file in a few ways, and one easy option is to move the file.
Moving it to a different directory can make it harder for hackers to find.
You can also modify the file so that visitors can’t access it.
Move the file to a private directory, whether you move the original file or modify it.
Fortunately, you should only have to do this once to help secure the file.
However, someone may be able to get into your site and find the new location.
When that happens, you’ll need to move the site again.
If you set up more WordPress sites, you’ll want to do it for each of them.
With each new site, only grant access to the file to people you trust.
Update Security Keys
Since the wp-config.php file holds certain security keys, they can be vulnerable.
Your site has four security keys, and they help make your login details hard to decode.
If you think a hacker got into your files, you should update the keys.
That way, you can keep the hacker from getting back into your site and doing more harm.
Use a generator to get new security keys.
Then, go into your file and edit it to include the new security keys.
19. Use Captcha Verifications Where Possible
CAPTCHA forms are super annoying, but they work very well.
Having to type in those random letters or choose silly pictures in boxes are just the latest defence when it comes to security, bots and hackers.
Knowing how to set these options up on your site and where is also half the battle.
For example, it’s definitel a good idea to add a CAPTCHA to the main log in page for your WordPress dashboard.
Another good location is on any forms that you might have on your site.
By leaving these forms open with a generic submit button only, not only will you see a lot more spam come through, there are also options for security leaks and robot hacks as well.
20. Add Security Headers
Security headers can help protect your website from some of the most common attacks.
For example, you can use an X-XSS Protection header to fight off cross-site scripting.
Others can help ensure your site redirects to HTTPS.
You can add security headers using Cloudflare or Sucuri.
Another option is to use a plugin, such as Redirection.
On the Site page of the plugin, scroll down to HTTP Headers.
Then, you can add headers to protect against cyberattacks.
If you have access to the server, you can also use the .htaccess file.
Use an FTP client to connect to your website, then you can add the necessary code to your file.
Save your changes to make sure everything works properly.
You can check the security with a tool called Security Headers.
It’s free to use and can tell you if there are any headers it detects.
If it doesn’t show the headers you entered, you’ll know to go back to your site and update the changes.
21. Implement WordPress Security Plugins
Another excellent option is to install a WordPress security plugin.
You can find many free options, such as Wordfence, which offer plenty of features.
Some of these plugins even cover various security steps in this list.
For example, Wordfence can help scan for malware and track your activity.
Then, you can get rid of plugins that only do one or two things.
That can further help keep your website running smoothly.
You’ll have fewer plugins to worry about and keep up to date.
Some general security plugins also have better support and more frequent updates.
All of that can help you keep your site in good shape and protect against hackers.
Now, some security plugins cost money to access more features.
However, you can usually test them out for free to see if you like how the plugin works.
If you don’t like one option, test another one until you find the program you like.
22. Use a VPN and Other Secure Connections
A virtual private network (VPN) can help keep your website secure.
It hides your computer’s IP address using an encrypted server.
Using one can be especially beneficial if you frequently work on your site in public.
Hackers could use public WiFi to figure out the name of your website.
Then, they could use that information to hack into your site.
If you allow others to access your website, you can also give them access to your VPN.
That can help keep people around them from getting into the site.
You’ll be able to work from wherever without as much of a risk of cyberattacks.
Now, VPNs can cost money, but many companies offer fantastic discounts.
You can try the service to see if you like it, and you can switch to a different VPN if you choose.
If you can’t use a VPN, use a secure WiFi network, such as your home connection to minimize security risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
WordPress security is a big deal, and you might still have questions about it.
Consider the following queries and the details to help learn more about WordPress site security.

Why is WordPress hacked so much?
Some common reasons WordPress is hacked include insecure web hosts and weak passwords.
Old versions of WordPress and its plugins can also lead to more hacks.
Also, about 43% of all websites use WordPress, so hackers probably have more practice with it than other systems.
What percentage of WordPress sites are hacked?
Hackers attack about 500 WordPress sites per day.
Since 455 million sites use WordPress, that means about 182,500 sites get attacked each year, or roughly 0.04%.
How do I check if my WordPress site is secure?
The best way to check if your site is secure is to run a security scan.
Many plugins let you do this, and they can check for vulnerabilities.
Then, you’ll know if your site is secure and if not, what you need to do.
You can also check yourself by reviewing your SSL and updating any themes or plugins.
Wrapping Up
WordPress security is vital if you want to keep your website running smoothly.
The software is common and can be an easy target for hackers.
Fortunately, you can use many plugins to help protect your site.
Just be sure you update those plugins regularly so that you don’t give your site more vulnerabilities.
If you still have questions about keeping WordPress secure, leave them below.
Securing your WordPress site doesn’t have to be hard.
But if you don’t do it, hackers could ruin your site.






